What is Calculus Bridge? Its Types, Causes, Effects, Prevention, and Treatment
Food is important because it aids survival. It serves as the fuel that aids the growth and development of your organs and other body parts. But, as you eat, a conducive environment is produced for the growth of bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria react with saliva to form a thin, sticky film, plaque, on the teeth. Plaque can not be totally avoided, however, regular oral hygiene such as brushing, flossing and mouth rinse can reduce its accumulation.
Foods rich in sugar and starch such as cakes, candy, soft drinks, and milk contribute greatly to the growth and formation of plaque. Plaque bacteria grow rapidly and develop into Calculus– a threat to your oral health. Plaque can harden into calculus within four to eight hours. However, it takes about 10 to 12 days to mineralize. So keep reading to find out more about how this plaque changes into Calculus Bridge.
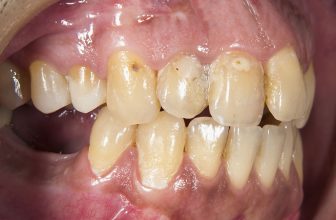
What is Calculus Bridge?
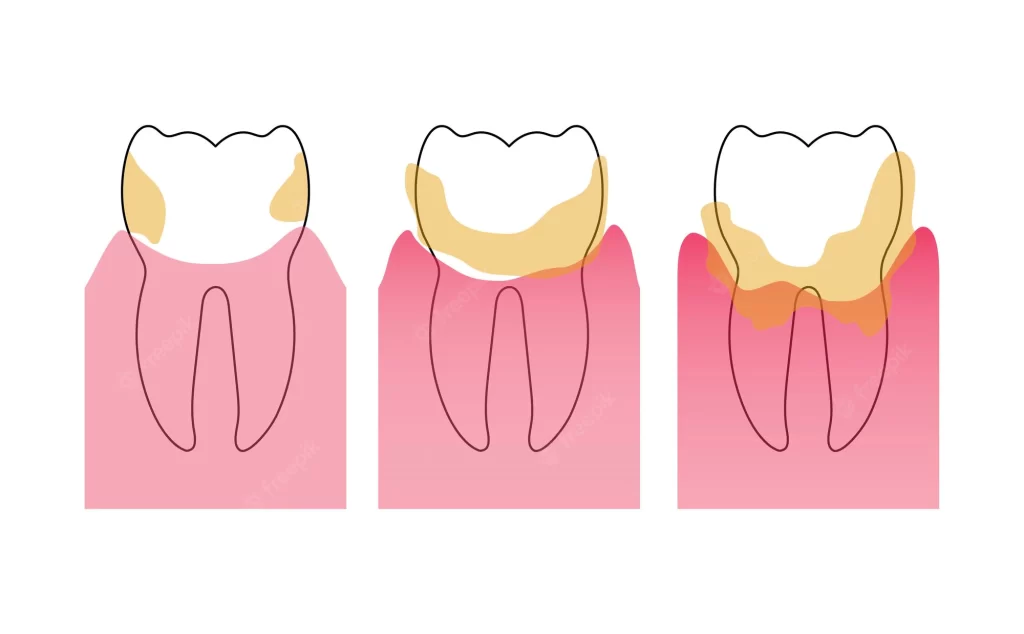
Calculus, also known as tartar, is a yellow, tan, brown, or white deposit of minerals found on the tooth’s surface. It’s formed from pre-existing hardened plaques. The formation of calculus differs in individuals. This condition is dependent on the pH of your saliva and the quantity of calcium and other substances present in your saliva. If not treated, calculus forms a bridge taking over multiple teeth, spaces between them, and the gums.
Calculus bridge is commonly found on the upper molars and lower anterior teeth due to their proximity to the ducts of the salivary gland.
Types of Calculus Bridge
Calculus bridge is classified into two based on their location;
Supra-gingival
It’s formed along the gum-line and found above the gum. It’s common on the surfaces of upper jaw molars and lower incisors. It’s visible and has a yellow or tan colour.
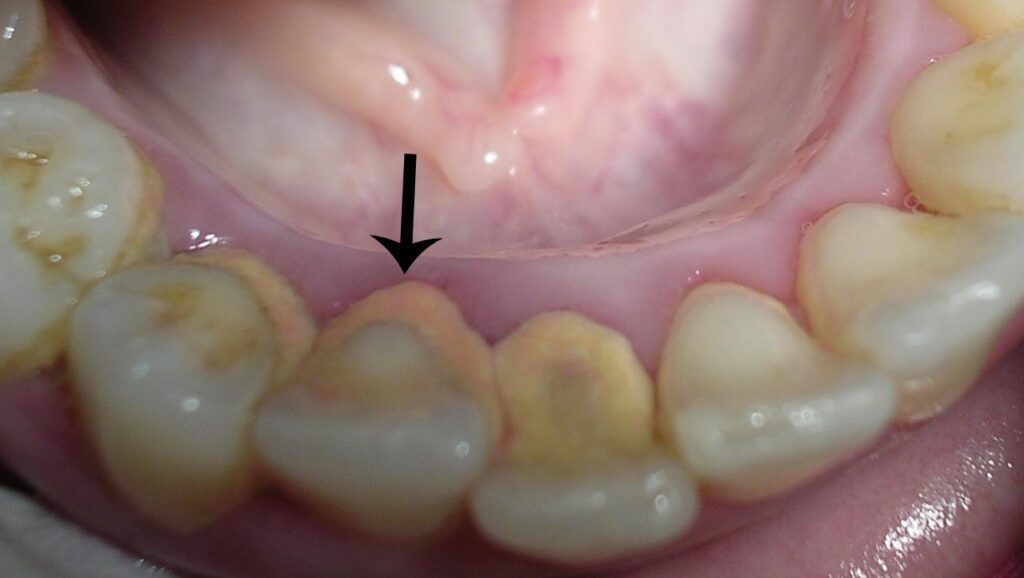
Sub-gingival
This is formed between the teeth and the gum. It’s mostly found below the gum. It’s not easily seen and can be detected using an explorer- a dental instrument. The bridge formed is dark due to the presence of black-pigmented bacteria.
Effects of Calculus Bridge
- Causes bleeding gums, the first sign of gingivitis and inflammation of the gums. Severe gingivitis can result in a severe infection known as periodontitis which causes the weakening of gums and falling out of the teeth.
- Persistent bad breath – Halitosis: Presence of tartar or calculus aids the multiplication of bacteria in your mouth which results in bad breath.
- Loss of tooth: If calculus is not treated immediately, it can develop into gum diseases, resulting in tooth loss.
- Receding gums: Your gums will start to recede when affected by Calculus Bridge. This exposes your teeth to more bacteria on the long run. The bacteria fill up the spaces between your teeth and gums, and the more bacteria in your mouth, the faster the rate at which tartar forms.
- Presence of cavities – tiny holes in the teeth: Tiny holes are formed on the enamel following a calculus bridge condition. These holes creates a passage for acid and bacteria, and then develop into cavities after a period of time.
- Tooth decay, and
- Tooth infection
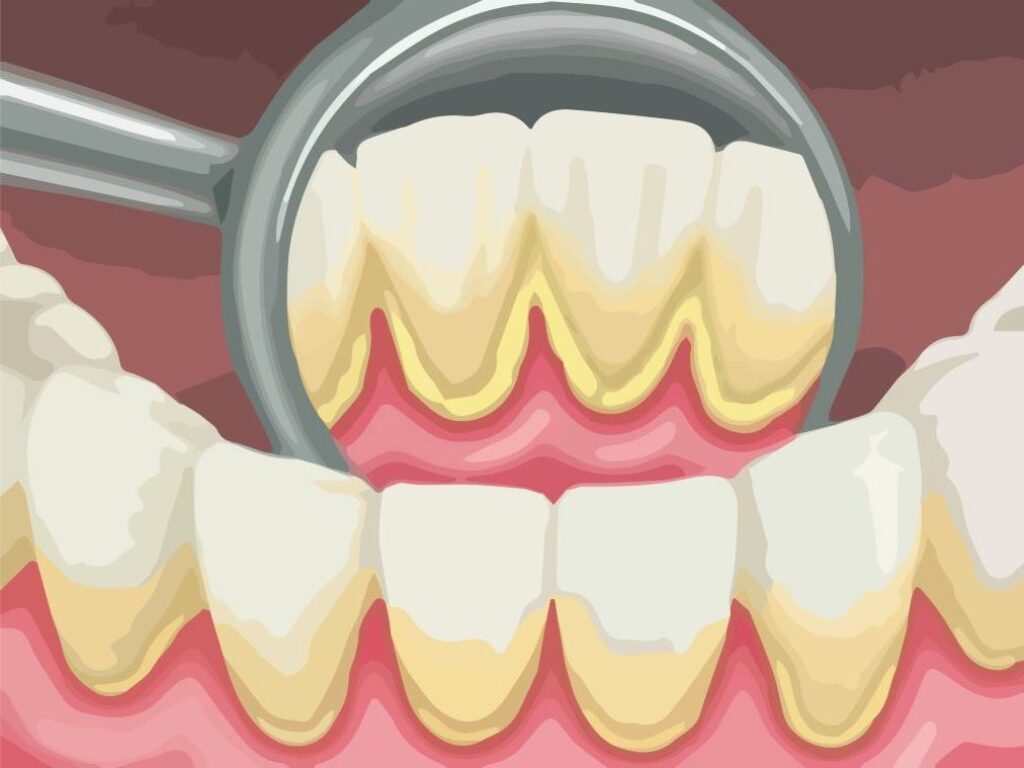
Causes of Calculus bridge
Although plaques can not be totally avoided, you are more at risk if you do the following :
- Smoke
- Consume coffee or tea
- Excessively consume chocolates and sweets: Chocolates and sweets are rich in sugar and sugar serves as a conducive environment for the breeding and growth of bacteria.
- Frequent consumption of unhealthy foods or junks.
- Irregular cleaning of the teeth
Prevention of Calculus Bridge
Calculus bridge can be prevented with the following tips;
- Brush your twice daily with a toothpaste containing fluoride. Make sure that you spend at least 2 minutes for brushing your teeth and gums.
- Regular cleaning in between the teeth.
- Change your toothbrush regularly: It is advisable that you change your toothbrush at least once in every 3 months. Although you can change it earlier, it all depends on your choice and usage. Ensure you replace them once you notice that the bristles are worn out. This practice is good for your oral health.
- Reduce sugar consumption: The less the sugary items you consume, the less the reaction of bacteria with sweet leftovers in your mouth.
- A regular visit to the dentist or dental hygienist : Regular dental cleaning and examination reduces your risk of oral diseases. The chances are that your dentist will easily find calculus in its early stage and the good news is that early discovery leads to early prevention and treatment.
- Remove plaque before it forms a bridge.
- Use a toothpaste containing triclosan. Triclosan helps to control the formation of calculus bridge.
- Regular flossing: You need to be careful while flossing, because improper flossing can cause damage to the teeth and gums. Hold the floss correctly between teeth and gently slide from tooth to tooth.
- Use of antimicrobial mouthwash: This helps to reduce the number of bacteria in your mouth. A mouth wash containing fluoride and free from alcohol is your best choice when choosing a mouth wash. Gargle the mouthwash in your mouth for some minutes and ensure you do not rinse out the water immediately. This gives the ingredients in the mouth wash enough time to work in your mouth.
- Consume foods rich in vitamin C. Foods rich in Vitamin C helps to remove bacteria and bad breathe from your mouth.
- Eat healthily
- Drink lots of water
Treatment of Calculus Bridge
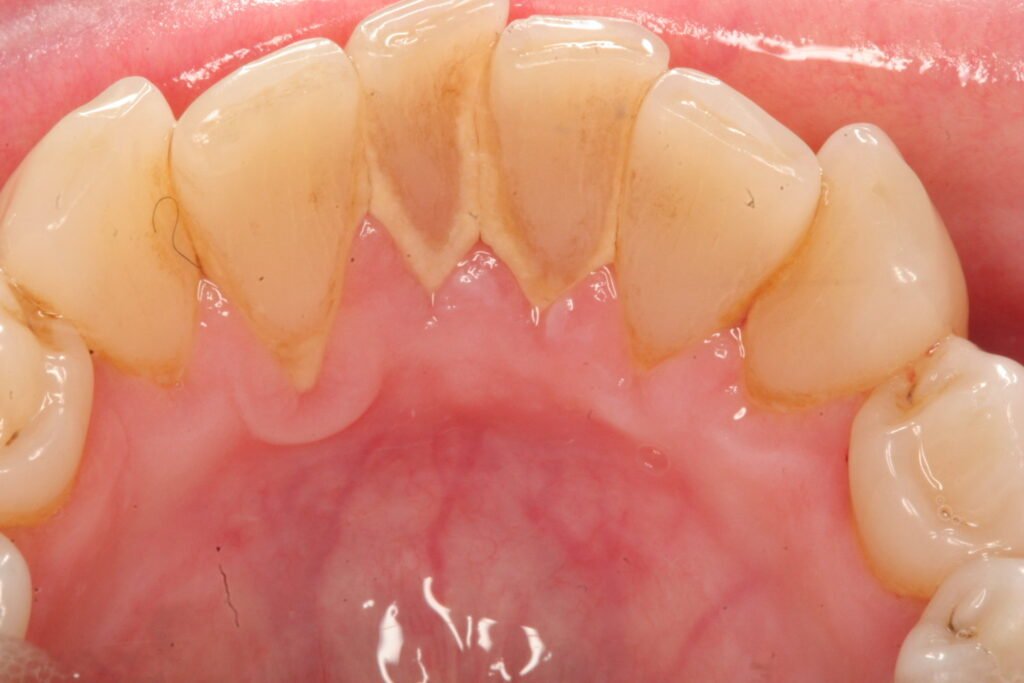
Calculus can be treated using professional scaling, cleaning, debridement, or root planning. It develops below the gum-line, and special instruments are used for treating this condition. Regular dental cleaning is done if your teeth are not affected by bone loss or periodontitis. Here, the dentist uses a scaler to scrape the hardened plaque between your teeth and around your gums.
Debridement is done if you have dense calculus that prevents your dentist from performing an oral evaluation. Then, ultrasonic instruments are used to break and remove the calculus.
Scaling and root cleaning can be performed if the calculus bridge has developed into gum disease. The dentist carries out this procedure using local anaesthesia to remove the plaque and calculus. After that, root planning is carried out, and the root surfaces of the teeth are smoothened out for the reattachment of your gums to your teeth. This is pictorial representation of how to use mouthwash.
To find the periodontist working in Ontario, you may follow this link.
To find the list of independent dental hygienist in Ontario, Canada, you can visit this link.